Six Sigma projects are primarily focused on customers. The other areas that Six Sigma projects focus on are:

- Improving the performance of Critical to Quality (CTQ)
- Reducing the number of complaints from customers.
- Reducing in-process or internal defects.
- Reducing warranty claims.
- Improving survey and customer research scores.
- Capturing feedback from staff members effectively.
- Increasing profits and revenue.
- Improving audit scores.
- Improving process performance and dashboard metrics.
- And, having better growth than competitors.
Tags
While leaders strive to build a culture of continuous improvement (CI) in their organizations, it is equally important to understand that business-as-usual activities take precedence over improvement activities. CI programs commence with a big bang and a lot of enthusiasm, but time wears out even the strongest and what it leaves behind is mere CI hubbub. This is not a simple problem to solve. If you have been part of any enterprise-wide CI deployment, you will have no difficulty relating to this. This problem is complex and has several failure modes.
In this article, I’ll like to highlight a common but significant failure mode – Selection of projects. It’s needless to emphasize that projects play a big role in any CI journey, but to its disgrace, projects are also a significant contributor to the downfall of CI program.
Going overboard and having too many concurrent projects is one way to fail. Not selecting the right projects to pursue is another. Here are few compelling reasons to consider project selection as an important activity rather than opening the floodgates of projects:
Business Priority: Every business has its own priorities and so it’s important to select the right projects that are aligned with your priorities. Having many dispersed projects will blemish, if not nullify the impact of projects. Alignment between leader’s priority & CI program can be easily accomplished if you select projects right at the beginning.
Change due to competition: If your competition is disrupting the industry, well you better select where you need to improve. External environment often forces organizations ruthlessly reform their way of thinking and working. And today, we all live in a world that is fast changing. So unless your right projects are selected and pursued, your CI program will become redundant soon.
High Customer Expectations: Everyone I talk to says, customers are demanding more than ever before. Understanding the changing their needs and aligning the CI program to customers is vital to the success of any organization’s CI program. Organizations sometimes pursue trivial opportunities such as cost saves but miss on acting on big ticket customer facing projects or customer pain points. Of course, while dealing with customers, things are going to be volatile, but that’s not a reason to avoid them. The good project selection process should filter such project opportunities.
Limited Budgets: All organizations must work within the framework of budgets. Improvements need monetary resources to support the change. Sometimes they are direct and hence easily associated to direct cost centers. But projects with intangible benefits or the ones incurring indirect costs usually end up as scapegoats. If an organization commits to project selection, many such failures can be prevented.
Availability of Resources: Human capital is scarce. CI projects need quality time and mindshare from people of importance in the organization. Quite often resource requirements are never considered during the commencement of projects. Even if considered, it’s only the project leader’s time. As CI projects are a cross-functional effort, active participation of experts from all involved functions defines the success of the project. In order to ensure we get the best out of our teams, we need to time our success. Thus project selection is a time sensitive activity.
Optimizing Number of Projects: Not all the areas of your organization need improvement at the same time, And improvement culture building is a slow and steady process which can never be implemented overnight, nor will the results reap overnight. So getting to rush out the organizational adrenaline may not be a success recipe for good CI program. Selection of projects will ensure that you sustain optimum enthusiasm in the system for CI.
So it is very evident that selection of projects impacts the CI culture, employee satisfaction, alignment to customers and ROI to business for the investments it makes in CI in a positive way. In the future articles, we’ll take this one step further and talk about the criteria used for selecting projects.
Tags
Have you ever confronted a situation doing hard work the whole day and at the end you realize that most of the time had been given by you and your team to the Non Value Added things! 
One of the important aspects of the leadership in today’s competitive world is Prioritization. It helps to save time and money as you will be able to focus on what is important at the expense of lower value activities. Prioritizing skills are your ability to see what tasks are more important at each moment and give those tasks more of your attention, energy, and time.
We all have so much on hand to do and really speaking so much time to finish the things up. But we lack the skill to manage our work with the time. We mostly forget to take up the important things first and less significant work later. Instead, we do completely opposite to this. This is human nature as we all do the same thing in our day to day lives.
This issue is pertinent not only at an individual level, but even at organizational level. Organizations focus on the wrong reasons or causes and waste a lot of effort to solve a problem or improve their business.
How to improve upon it?
Lean Six Sigma teaches a very useful technique of prioritization to overcome this problem which is a mother of our all the other problems.
Pareto Analysis is based on 80/20 rule which says that our 20% efforts (out of the whole 100%) will give 80% of the benefits. This can be interpreted in many different ways like, for sales people 80% of the orders will come from the 20% of the customers, for team managers 20% people of the whole team shall give 80% of the work or results. Here, we should keep in mind that this doesn’t mean that the rest 20% is not important at all but can be said as less significant.
To generalize, 80% of the problem is caused by 20% of the reasons!
Thus using the Pareto principle, we can derive maximum impact with minimum effort and within short time span, if we focus on the right factors. Simple it is, right?
Before understanding the benefits of Pareto Analysis there are certain facts to be known about it. They are as under:
- This principle was developed in the year 1896 and is named after Vilfredo Pareto who was an Italian engineer, sociologist, economist, political scientist, and philosopher.
- Pareto derived this concept by his work and experience and observed that 80% of the wealth in Italy belonged to 20% of the people.
- In the year 1941, Dr, Joseph Juran who was an evangelist of quality and quality management as he was an engineer and a management consultant cam across the concept of Pareto Principle. He then started applying the principle in the quality and derived a phrase through experience that is “there are vital few and useful many”.
- The Pareto Principle can be implemented in many different aspects such as in science, management, business, in software, in sports, occupational health and safety, financial service industry, and implementing projects which says that put 80% of your time in 20% of your project which will save a lot of your time and energy.
- Pareto principle can be graphically represented by Pareto Chart that contains bothbars and a line graph, where individual values are represented in descending order by bars, and the cumulative total is represented by the line.
With an example given as under you will be able to understand why to focus on significant few:
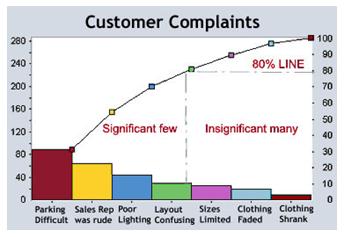
Our Online Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course teaches you step by step procedure to construct a pareto chart, different pareto variants and how to interpret them. More importantly it covers when and when not to apply pareto principle.
Benefits of Pareto Analysis:
- Improved Decision Making: With a focus on resolving problems, the procedures and processes required to make the changes should be documented during a Pareto analysis. This documentation will enable better preparation and improvements in decision making for future changes.
- Increased Efficiency: Once the changes or problems are listed, they are ranked in order from the biggest to the least severe. The problems ranked highest in severity should become the main focus for problem resolution or improvement. Focusing on causes and problem resolution contributes to organizational efficiency.
- Enhanced Problem Solving Technique: Members of a group can conduct a Pareto analysis together. Arriving at a group consensus about the issues that require change fosters organizational learning and increases group cohesiveness. Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course shall help the individuals of the company learn many tools along with Pareto Analysis which shall also help him or her to boost their careers.
- Saves Time and Money: Doing right things at the right time with right people and at the right place is naturally going to save time and money and this has to be calculated by multiplying the time with the number of individuals involved in the process.
Tags
As we all know that there are different levels of certification in Lean Six Sigma and these levels have been associated with “Belt” titles. It’s a very obvious question that why the levels here have been associated with the titles used in Martial Arts? That is because of the association of discipline and rigor in Lean Six Sigma similar to the martial arts.
You would find four commonly used belt titles in Six Sigma Certification and they are Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt and Master Black Belt. However, the most basic level in Lean Six Sigma is sometimes called as “White Belt”. A White Belt understands the theoretical aspects but virtually no application knowledge of the Lean Six Sigma concept. One could say this is an entry level awareness program. Let us understand one by one, the four belts mentioned above.
- Yellow Belt: A Yellow Belt is someone who has undergone a basic training program that is may be a day’s training with a basic level of understanding of the quantitative part of the concept. He or she is able to appreciate the goals of Lean Six Sigma. Having knowledge of Yellow Belt level means that person is able to apply basic tools in the company and undertake simple improvement projects. Usually the organization who wants to implement Lean Six Sigma wants all their employees to be at least Yellow Belt trained as this makes the implementation and change management easier and faster.
- Green Belt: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt receives a training of at least one week with emphasis on DMAIC method and tools. DMAIC is problem solving methodology which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control through which he/she is able to undertake improvement projects in his/her process which improves customer satisfaction and efficiency of the process. Green Belts are also called as “Work Horses” having the following responsibilities:
- Initial analysis of company like Gemba Walk and Data Analysis which will be helpful in defining the road map of the project.
- Define the project and prepare the project charter.
- All over co-ordination with management, yellow belts, black belts and master black belts.
- Facilitate the team through all phases of the project.
- Provide training to the team for effectiveness of the implementation.
- Black Belt: A black belt is someone who receives at least 3 to 4 weeks of extensive training with the emphases on DMAIC method and tools which is explained as above. Unlike a green belt, black belt is a full time role who has the responsibility to run large scale high impact improvement projects where he mentors and coaches green belts. Responsibilities of a black belt are listed as under:
- Helps in deciding the project.
- Helps in refining the project charter and makes sure that the things are moving in the desired direction.
- Leads, mentors and coaches green and yellow belts and champions.
- Empowers the team members to design experiments and analyse the data required for the project.
- Provide training in tools and team functions to project team members.
- Makes sure that the project succeeds.
- Maintains balance between Management, Employees and Customer’s needs.
- Manages the team for effectiveness and efficiency.
- Master Black Belt: It is usually a leadership role having excellent change management skills along with having good technical knowledge. After completion of the black belt course and having good experience he/she receives additional 3 to four weeks of training mostly around change management and statistics. MBB’s primary role is to deploy six sigma concepts in the organization, advice to executives or business unit managers, and leverages, his/her skills with projects that are led by black belts and green belts. A Master Black Belt reports the senior or top management and coaches the black belts and Green Belts. Responsibilities of Master Black Belts are enumerated as under:
- Provides guidance to senior executives and top level managers on Six Sigma management.
- Help identify and prioritize key project areas in keeping with strategic initiatives.
- Continually improve and innovate the organization’s Six Sigma process.
- Apply Six Sigma across both operations and transactions-based processes such as Sales, HR, IT, Facility Management, etc.
If you want to start your journey in Lean Six Sigma, its best you start by understanding some of the basics of Lean Six Sigma. Our Lean Six Sigma Primer Course is Free and it gives a great deal of information on Six Sigma. From there on you could more to Yellow Belt and Green Belt. This approach is pragmatic because it optimizes your investment of resources, time and effort.
Tags






