To gather the VOC, effective methods for accurately capturing customer requirements are required. Several methods are available to capture the VOC.
- Interviews are used to gather information from stakeholders by talking to them directly. Interviews aid in identifying and defining features and functions or desired project deliverables.
- Focus groups is a trained moderator-guided interactive discussion that includes pre-qualified stakeholders and subject-matter experts (SMEs) to elicit their expectations and attitudes toward the proposed product, service, or result of the project.
- Facilitated workshops is an interactive group-focused sessions that bring together key cross-functional stakeholders to define the project or product requirements. It is a primary technique to define cross-functional requirements and reconcile stakeholder differences to the project. Facilitated workshops occur much faster than individual discussions.

- Questionnaires and surveys is another method where written sets of questions designed to quickly gather information from a broad audience.
- Mystery shopping commonly performed in retail industries. This method is used to measure the quality of a service by gathering specific information about the product or service. This method is performed by mystery shoppers who introduce themselves as customers and perform specific customer-related tasks, such as purchasing a product and raising questions and complaints about the product.
- Observations are a direct way of viewing individuals in their work environment or while using the product to identify the project or product requirements. Also referred to as job shadowing.
- Market research is an organized effort to gather information about the current trends in an industry and also Field reports is a formal report documented by field engineers or other on-site personnel who gather required information about events that occur during their field work.
- Customer feedback and complaints data are used to gather customer requirements. This method also involves gathering customer feedback about the quality of a product or service. The consolidated list of feedback from customers is referred to as complaints data.
- Reliability data is a source of information that helps in analyzing the reliability of a product or process. By gathering this data, you can plan strategies to gain a reputation with customers as a reliable provider of services.
- Staff feedback is another method of gathering opinions from staff who interact with customers directly or who possess knowledge about customers and their expectations. This information is captured by conducting surveys, brainstorming sessions, and other information gathering sessions.
Tags
Another roadmap of DFSS is DMADV, an acronym for five interconnected phases, namely Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify. This methodology is used in projects that involve creating a new product or process design.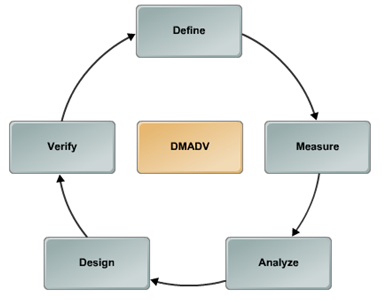
Define – The project goals are defined so that they are in line with customer requirements and enterprise strategies.
Measure – Characteristics that are critical to quality as well as product and process capabilities are measured.
Analyze – The different process options are analyzed and the best process that is consistent with customer requirements is selected.
Design – The details of the process are designed and optimized to meet the needs of customers followed by the performance of the new design which is tested through pilot runs before implementation.
Verify – In this phase the results are test and implementation of new design is carried out for large scale deployment.
Tags
Define Phase is the first phase of Lean Six Sigma Project. Following are the deliverable of this phase:
- Develop the Project Charter
- Identify the Project CTQ
- Create Process Maps
Develop the Project Charter
Project Charter is an important document that summarizes the purpose, current scenario & goal, measures of success (CTQ), project’s scope, quantitative & indicative project benefits, and team members. This is the most important document, as it creates a term of reference for this entire Lean Six Sigma project. In order to prepare the project charter, several meetings and preparatory steps may be needed. In some cases, gathering the Voice of Customer (VOC) may be required to even understand the problem.
Project Scoping determines exactly how the project will contribute to overall business, whether the efforts will be diverted to maximum impact area, team composition, financial resources required, etc. In Six Sigma, a tool called ‘In-Frame Out-Frame’ is used to decide on the scope.
Six Sigma Green Belt should closely work with the Project Sponsor to complete the Project Charter.
Identify the Project CTQ
CTQ refers to Critical to Quality metric. This is a measure of success for the project. Usually, there is only one CTQ for DMAIC projects. It can either be a measure of efficiency or effectiveness. However, it is a key performance indicator for Voice of Customer or Voice of Business. Further, it should be measurable. Usually, its indicative or accurate current performance is reported in the project charter.
The above two deliverable run parallel, and they are of significant importance because they mark the formal kick-off of the project, team member induction, Lean Six Sigma training (if not included earlier).
Create Process Maps
In order to understand the end-to-end process; a detailed process document is created by the team. However, in case such documentation already exists, then it becomes easy for the project team members to revisit it.
Six Sigma Green Belt can involve all her team members in this activity. Two best ways of mapping a process are to interview all the parties involved in the process or to conduct a work-out session with all parties. Latter requires good facilitation skills.
Once the process maps have been created, the team can use them to identify the bottlenecks, challenges, issues, inputs & outputs, delays, etc. Essentially, it can be used to decide which part of the process is important, and needs to be introspected.
On completion of the above deliverable, a formal define tollgate review is conducted. Then the project moves to Measure Phase. Next >>>